What is Porosity?
Porosity refers to the phenomenon where cavities are formed inside the material during the casting process. It is considered a type of casting defect that negatively impacts the strength and durability of products. Therefore, preventing porosity is essential to avoid the production of defective products.
Causes of Porosity
The causes of porosity can be broadly divided into two categories:
- Gas Entrapment:
Mixed gases or air in the molten metal solidify during the casting process, forming cavities.
- Incomplete Mold Filling:
Poor flow of molten metal prevents the mold from being filled, resulting in hollow spaces.
Note: Molten metal refers to liquid metal at high temperatures.
In die casting, methods such as high-pressure die-casting, low-pressure die-casting, and vacuum die-casting are used to set conditions that prevent gas entrapment and optimize the flow of molten metal. However, achieving zero porosity is nearly impossible.
Other casting methods, such as sand casting and lost wax casting (investment casting), also carry the risk of porosity formation.
Types of Porosity and Measurement
Porosity can be roughly classified as shrinkage porosity and blowhole porosity.
What is Shrinkage Porosity?
Shrinkage porosity occurs due to solidification contraction, which reduces the volume of the metal as it transitions from a liquid to a solid state.
To prevent shrinkage porosity, it is necessary to supply additional molten metal to compensate for the volume lost during solidification. It is crucial to ensure that the supply route remains open throughout the solidification process.
What is Blowhole (Gas Porosity)?
Blowholes are larger round-shaped gas bubbles that occur in the metal during the casting process. These defects are caused by air and gas arising in the mould, staying and being solidified.
To prevent blowholes, changing the casting conditions and runner’s design, reducing remaining gas, and using a deoxidizer are also effective.
Pinhole refers to gas porosity, which is smaller than a blowhole.
Case Study: Identify the Causes of Porosity Through Aluminum Die-Casting
※This case study is referenced from the Work Scenario Working Group Action by IVI (Industrial Value Chain Initiative).
In this case, the clients had issues with porosity in aluminum die-casting:
- They kept finding porosities when they used different die-casting machines under the same conditions.
- They did not comprehend certain causes of the porosities.
Solution
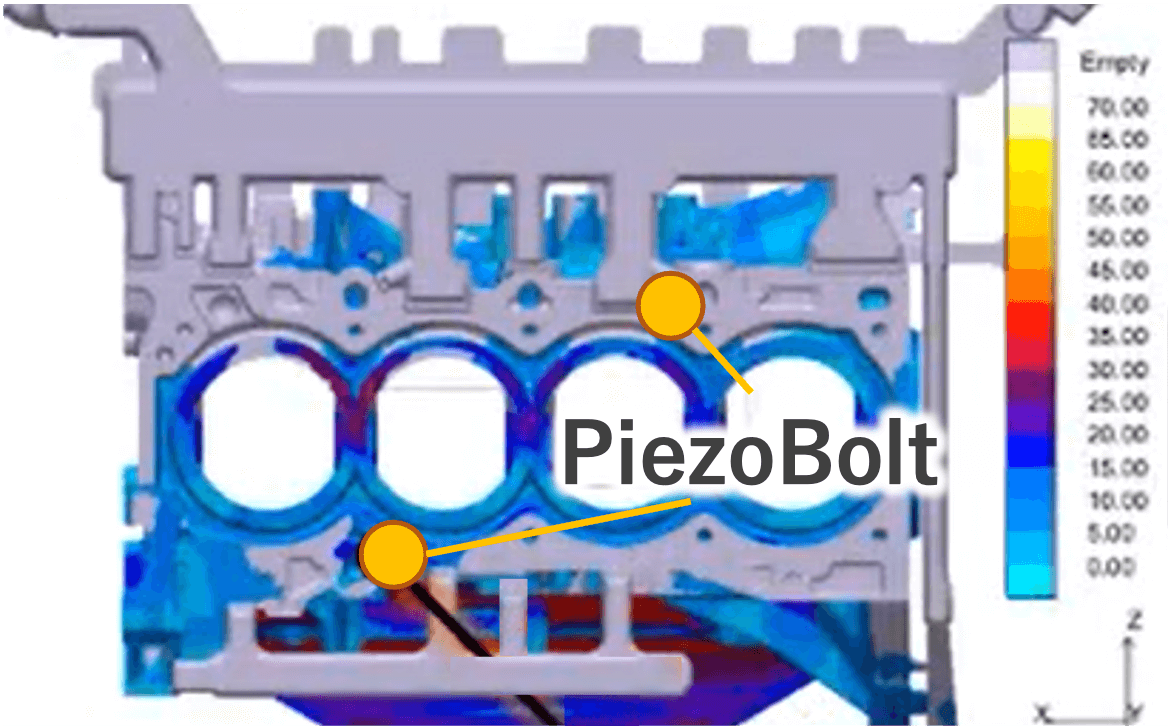
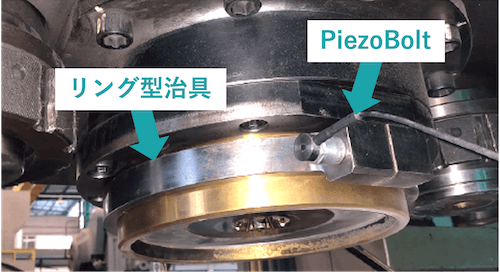
As a solution, we mounted two piezoelectric load sensors known as “PiezoBolts” in the machine to monitor the pressure applied to the ejector pins.
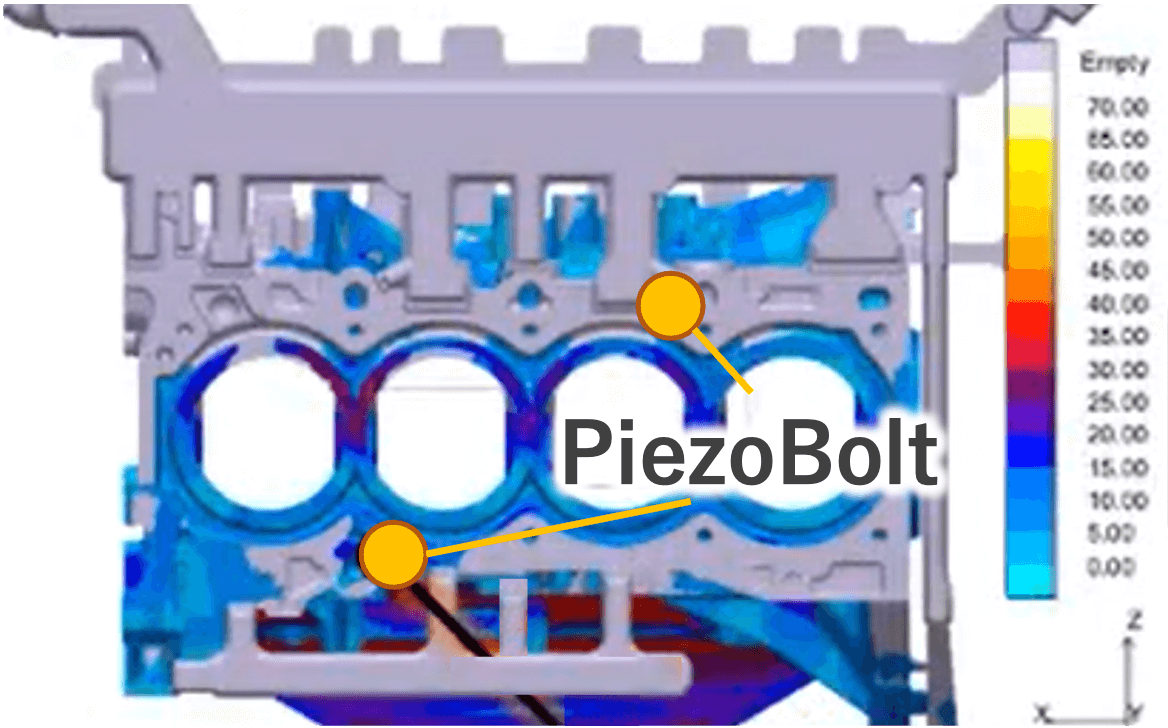
※What is the Bolt Piezoelectric Load Sensor “PiezoBolt”?
“PiezoBolt” is the load sensor with an embedded sensor unit using a piezoelectric element inside the bolt. It is capable of measuring minute load changes by leveraging the piezoelectric effect, which generates voltage when force (pressure) is applied.
For more detailed information, please click the link below.
Result
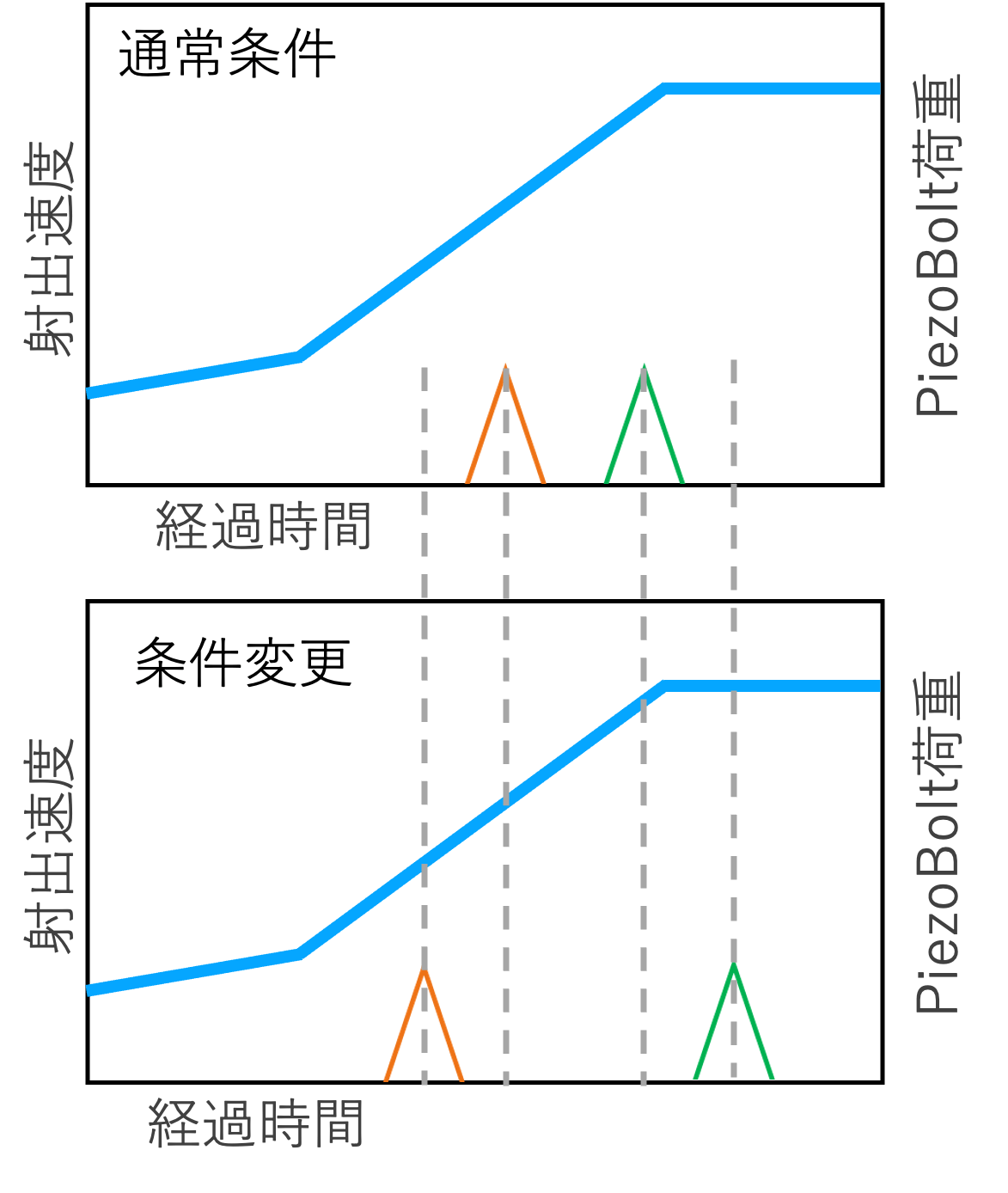
As a result, we discovered that the timing of pressure increases varied due to differences in the temperatures of the molten metal and the molds.
This timing discrepancy also allowed us to identify the cause of porosities, which occurred due to trapped gas in the molten metal. The time lag altered the flow of the molten metal, preventing the gas from escaping completely.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading.
There are several methods to prevent porosity, and this time we have introduced a solution using our load sensor. Our monitoring solution system has been successfully implemented in factories that use various processes beyond casting, including forging, machining, and press forming.
If you are considering introducing this solution to your production site, or having troubles with defects, please contact us.